11 Authentication of the pathogens
11.1 Introduction
In this part, we will start authenticating the pathogens found by the krakenuniq tool. This part is complex and needs database dependencies to work. So we will focus only one microbe (taxid 2047) from the sample sample1.
We will run an sbatch script, and we will check the outputs. Before working on this part, lets export the PATH variable to check the output files:
export PATH=${PATH}:/truba/home/egitim/miniconda3/envs/aMeta/bin/The main logic in this section, is to:
- Get information of the scientific name and sequence id information of the particular microbe
- Extract DNA reads assigned to one specific microbe
- Calculate several authentication parameters from the
sample1.trimmed.rma6file - Create a
bamfile from thesample1.trimmed.sam.gzusing the sequence id of the microbe - Extract read length, breadth of coverage, and post-mortem decay parameters from the
samfile - Combine these information into nice looking pdf file
- Calculate the authenticatio score for the particular microbe
First, let’s run the sbatch script, and then we will start checking the main output files while it is running:
sbatch Authentic.sh --account=egitim ## Scientific name and sequence ID extraction
Let’s go step by step.
In the krakenuniq part, we created a file called taxID.pathogens.
Let’s check this file:
less /truba/home/egitim/aMeta/results/KRAKENUNIQ/sample1/taxID.pathogensAfterwards, we will extract the node name from the krakenuniq database. We can not show the output, because it needs the big krakenuniq database.
Let’s check the output:
less /truba/home/egitim/aMeta/results/AUTHENTICATION/sample1/2047/node_list.txtTHis pathogen name is Rothia dentocariosa. Over the next steps, we will extract DNA reads assigned to this pathogen, and we will create authenticity metrics.
Then we will extract the sequence name of the reference sequence of the bacteria from the database:
/truba/home/egitim/aMeta/results/AUTHENTICATION/sample1/2047/name_list.txt11.2 DNA read extraction and postprocessing
Then we will use MaltExtract and postprocessing.AMPS.r tools to extract DNA reads assigned to this pathogen, from the rma6 file of the sample1.
Let’s check this folder:
ls /truba/home/egitim/aMeta/results/AUTHENTICATION/sample1/2047/MaltExtract_output/The ancient folder contains statistics only for ancient DNA reads, and default folder contains statistics for all DNA reads.
If we check the default folder, we can see that several parameters are organized into sub folders:
s /truba/home/egitim/aMeta/results/AUTHENTICATION/sample1/2047/MaltExtract_output/modern/11.3 Creating a sam file for the microbe of interest
In this step, we extract alignment entries from the malt sam file using this sequence ID that we previously extracted,
Let’s check the output file:
samtools view /truba/home/egitim/aMeta/results/AUTHENTICATION/sample1/2047/sorted.bam | lessFrom this file, we will extract breadth of coverage and read length distribution information:
less /truba/home/egitim/aMeta/results/AUTHENTICATION/sample1/2047/breadth_of_coverage
less /truba/home/egitim/aMeta/results/AUTHENTICATION/sample1/2047/read_length.txtThen we extract DNA sequence of the reference file to use with IGV tool:
less /truba/home/egitim/aMeta/results/AUTHENTICATION/sample1/2047/CP009643.1.fastaWe calculate PMD scores:
less /truba/home/egitim/aMeta/results/AUTHENTICATION/sample1/2047/PMDscores.txt11.4 Combine authentication parameters and score
Using the authentic.R script, we create the last authentication plot:
ls /truba/home/egitim/aMeta/results/AUTHENTICATION/sample1/2047/authentic_Sample_sample1.trimmed rma6_TaxID_2047.pdfLets check the authentication plot:
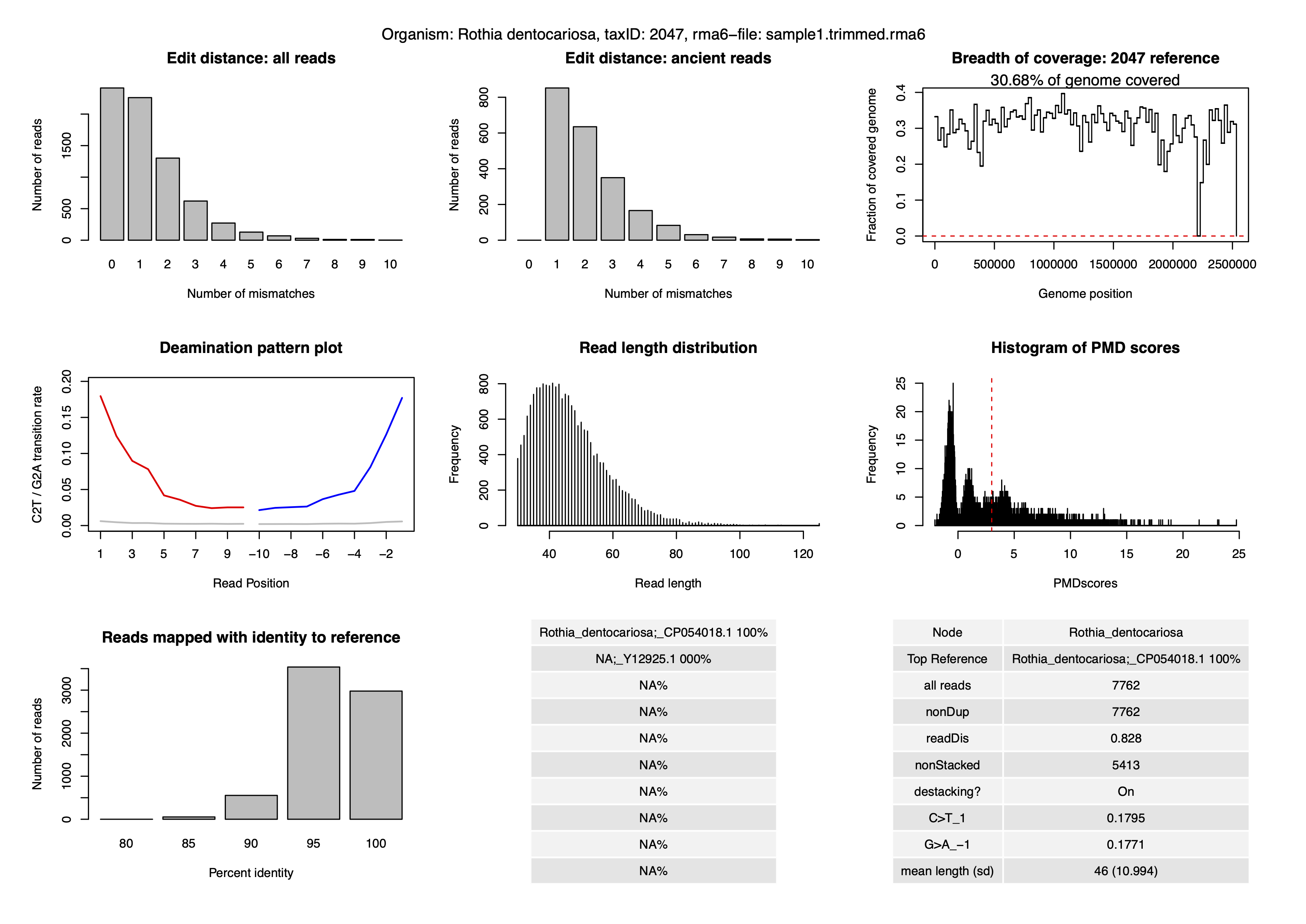
And at last, authentication scores:
less /truba/home/egitim/aMeta/results/AUTHENTICATION/sample1/2047/authentication_scores.txtThe script should have finished by now. Let’s check the output folder:
ls results/AUTHENTICATION/sample1/2047